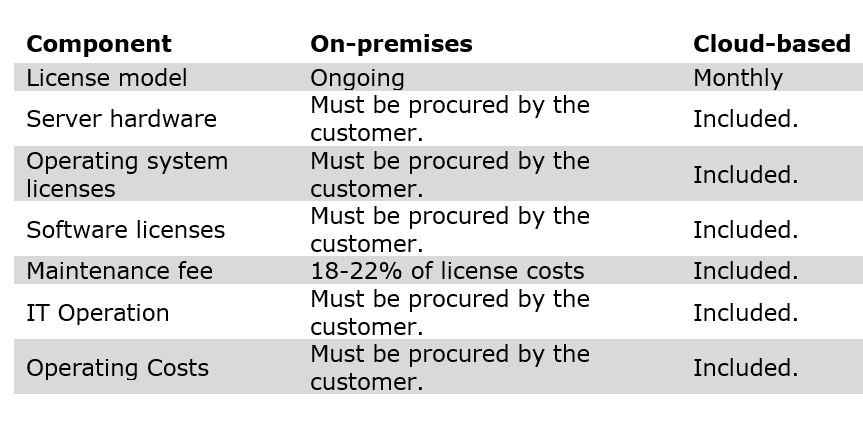
Public, private or on-premises?
In cloud computing, there are various ways to provide the infrastructure and services. The three main ones are the private cloud, public cloud and hybrid cloud:
A private (or corporate) cloud is, as the name suggests, a closed platform that is used only by one company or organization. It is usually hosted at its own data center (which requires the appropriate hardware), but can also be hosted by an external data center service provider. The system is your "private" system, i.e. you can basically do the same things as with your on-premises system (especially in terms of customizing, extensions and modifications).
In the public cloud, different organizations or cloud clients share the same IT resources when using the services. For a warehouse management solution, for example, this means that you can use a pre-configured system with best practice processes, but they can only be customized to a very limited extent. On the flip side, the software receives regular updates that all customers can use.
A hybrid cloud is a combination of a private and public cloud, where each organization decides which services it wants to move to the public cloud and which ones should be hosted in the private cloud.
So, which option is right for you? As a rule of thumb: Continue to map mission-critical processes using specialized applications in a private cloud or on premises. Processes that do not provide competitive advantages can be supported by standard systems that are provided as public cloud solutions.